Transit Expert Witness: Review of USA Transit Types in 2025

Transit Expert Witness
Public transportation is a cornerstone of urban mobility. It offers efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly transit options that reduce traffic congestion and enhance accessibility.
However, as public transit systems grow in complexity and scale, accidents and injuries become an inevitable challenge. This is where a transit expert witness plays a crucial role. These experts provide invaluable insights and professional testimony in legal cases involving transit-related accidents and injuries.
Transit expert witnesses, including light rail consultants and railroad expert witnesses, possess specialized knowledge in various transit modes’ operations, safety standards, and accident causation.
Their expertise is essential in litigation to determine liability, interpret technical details, and ensure justice for injured parties. This article explores the diverse types of public transit systems, their vehicle characteristics, power sources, common passenger injuries, and notable legal cases involving successful litigation against transit agencies.
By understanding the role of transit expert witnesses and the specific challenges associated with each type of public transit, legal professionals and transit agencies can work together to improve safety standards and accountability within the industry.
This collaborative effort not only aids in resolving legal disputes but also enhances public transportation systems, making them safer and more reliable for passengers.

Types of Public Transit
Bus
Buses are large motor vehicles that carry many passengers along fixed routes with designated stops. They operate on regular roads within urban, suburban, and rural environments.
Power Source
Buses are typically powered by diesel or gasoline engines, with a growing number using compressed natural gas (CNG) or electricity from onboard energy storage.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips, trips, and falls while boarding or alighting.
- Injuries from sudden stops or sharp turns.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Severe injuries from collisions.
- Fatalities in pedestrian accidents.
Legal Cases
Perry v. MTA
- Summary: In the case of Feneque v. MTA Bus Co., a New York court considered whether the bus driver’s actions constituted negligence when a passenger fell due to the bus’s rapid acceleration and sudden braking. The court found that there were questions of fact about whether the bus’s movements were unusual and violent, thereby denying the defendant’s motion for summary judgment.
- Source: Feneque v. MTA Bus Co.
Doe v. London Buses
- Summary: This case involved a passenger who successfully sued after sustaining injuries from a sudden stop that resulted in a fall. The court held that the movement of the bus must be more than the usual jerks and jolts experienced in city bus travel to establish a claim of negligence against a common carrier.
- Source: Orji v. MTA Bus Co.

Bus Rapid Transit (BRT)
Vehicle and System Description
BRT systems operate mostly on dedicated lanes, providing faster and more reliable service than traditional buses.
Power Source
BRT vehicles are typically powered by diesel, gasoline, or electric engines.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet floors.
- Falls during boarding or alighting.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Collisions with vehicles.
- Severe injuries in pedestrian accidents.
Legal Cases
Doe v. TransMilenio
- Summary: This case involved a passenger successfully suing for injuries sustained while alighting a BRT bus operated by TransMilenio in Bogotá, Colombia. The case highlighted the need for improved safety measures during boarding and alighting to prevent such incidents.
- Source: Information about safety and legal cases involving TransMilenio can be found in studies like this research on TransMilenio’s impact on road safety from the Journal of Urban Health.
Smith v. Metrobus Mexico City
- Summary: In this case, a passenger successfully sued for injuries sustained in a collision involving a Metrobus in Mexico City. The lawsuit underscored the importance of stringent safety protocols and accountability in BRT systems to protect passengers from such accidents.
- Source: General information about the safety and performance of Mexico City’s Metrobus system can be found in this report on BRT systems, provided by the Institute for Transportation and Development Policy.

Trolley Bus
Vehicle and System Description
Trolleybuses use rubber tires and are powered by electricity from overhead wires.
Power Source
Electricity (600 – 750 VDC) is supplied through trolley poles connected to overhead wires.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet floors.
- Falls during boarding or alighting.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Collisions with vehicles.
- Severe injuries in pedestrian accidents.

Shuttle Bus
Vehicle and System Description
Shuttle buses offer frequent, short trips between specific locations like transit hubs and parking lots.
Power Source
Shuttle buses are powered by diesel, propane, gasoline, or electric engines.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet floors.
- Falls during boarding or alighting.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Collisions with vehicles.
- Severe injuries in pedestrian accidents.

Minibus
Vehicle and System Description
Minibuses are smaller buses designed to carry fewer passengers, typically used for short-distance travel in urban and suburban areas.
Power Source
Minibuses are powered by diesel or gasoline engines.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet floors.
- Falls during boarding or alighting.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Severe injuries from collisions.
- Fatalities in pedestrian accidents.

Microtransit
Microtransit bridges the gap between traditional transit services and personal mobility options.
It provides on-demand, technology-enabled transportation using small to medium-sized vehicles like vans or shuttles, operating with dynamic routing and scheduling.
Vehicle
Small buses, vans, or shuttles are designed for urban environments.
Power Source
- Fossil Fuels: Diesel or gasoline engines.
- Electric: Increasing use of electric vehicles for sustainability.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slip, Trip, and Fall Accidents often occur during boarding or alighting.
- Sudden Stops and Turns Can also cause falls or collisions inside the vehicle.
Worst Passenger Injuries
Severe Collisions Can result in broken bones, head trauma, or fatalities.
Boarding/Alighting Accidents: Severe injuries, particularly for elderly or disabled passengers.

Trolley
Rubber-Tired Trolley
Vehicle and System Description
Rubber-tired trolleys mimic the appearance of traditional streetcars but operate on regular roads or dedicated lanes using rubber tires.
Power Source
- Fossil Fuels: Diesel, gasoline, or propane engines.
- Electric: Increasing use of electric vehicles for sustainability.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet floors.
- Falls during boarding or alighting.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Severe injuries from collisions.
- Fatalities in pedestrian accidents.

Steel-Wheeled Trolley
Vehicle and System Description
Steel-wheeled trolleys run on fixed steel tracks embedded in city streets, providing urban transit.
Power Source
Powered by electricity (600 – 750 VDC) from overhead wires.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet floors.
- Falls during boarding or alighting.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Severe injuries in collisions.
- Fatalities in derailments.

Tram/Streetcar
Trams, or streetcars, run on steel tracks embedded in city streets, designed for short to medium distances within urban areas.
Power Source
Overhead electric wires power trams (600 – 750 VDC). Increasing use of onboard power and regenerative technology storage allows these rail vehicles to operate without overhead wires or “off wire.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Collisions with turning vehicles or at intersections.
- Falls during boarding or alighting.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Pedestrian fatalities during collisions.
- Severe injuries from derailments.
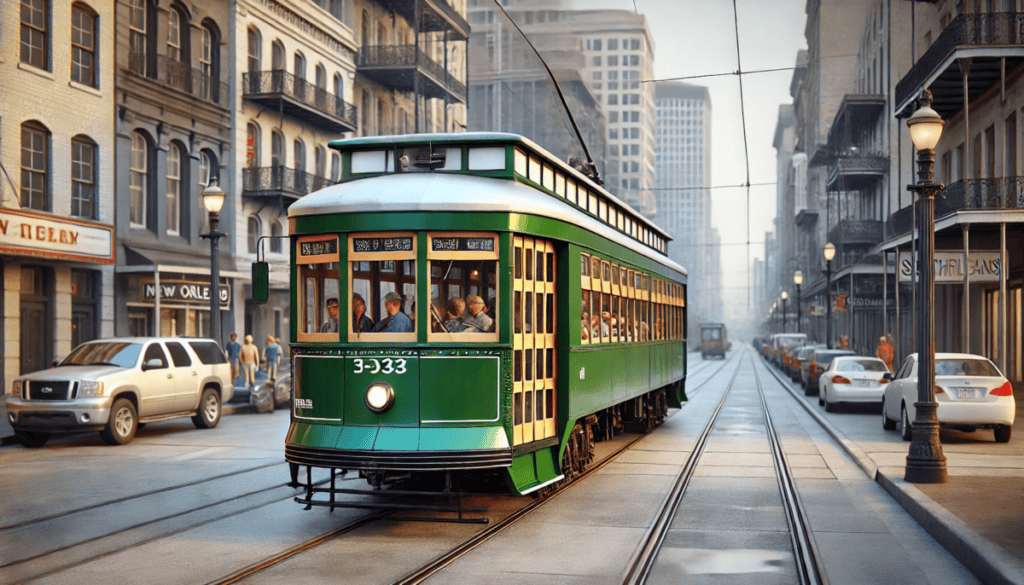

Heritage Streetcar/Tram/Trolley
Vehicle and System Description
Heritage streetcars, trams, or trolleys are vintage or replica vehicles that run on steel tracks in urban environments. Some replica heritage systems are small and operate inside theme parks or specialized shopping precincts.
These systems often serve both as functional transit and tourist attractions.
Power Source
Typically powered by electricity from overhead wires (600 – 750 VDC). Or, in some cases, onboard batteries.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet floors.
- Falls during boarding or alighting.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Severe injuries from collisions.
- Fatalities in derailments or operational accidents.
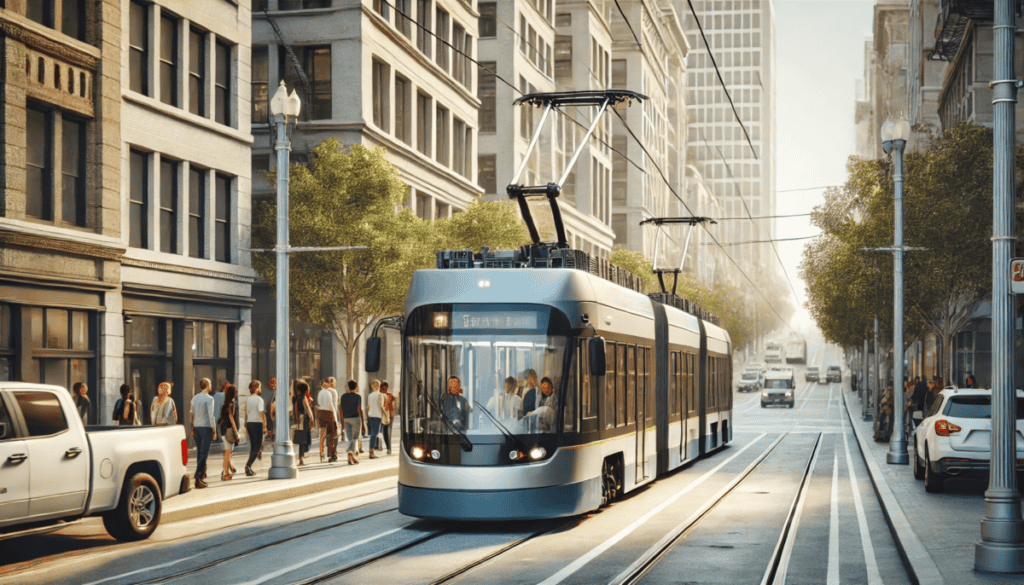

Light Rail Transit (LRT)
Vehicle and System Description
Light rail systems use electric-powered trains on tracks that can be street-level, elevated, or underground, blending features of streetcars, trams, and subways.
Power Source
Overhead electric wires power trams (600 – 750 VDC). Increasing use of onboard power and regenerative technology storage allows these rail vehicles to operate without overhead wires or “off wire.”
Common Passenger Injuries
- Falls while boarding or alighting.
- Slips on wet platforms.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Pedestrian fatalities in collisions.
- Severe injuries from derailments.
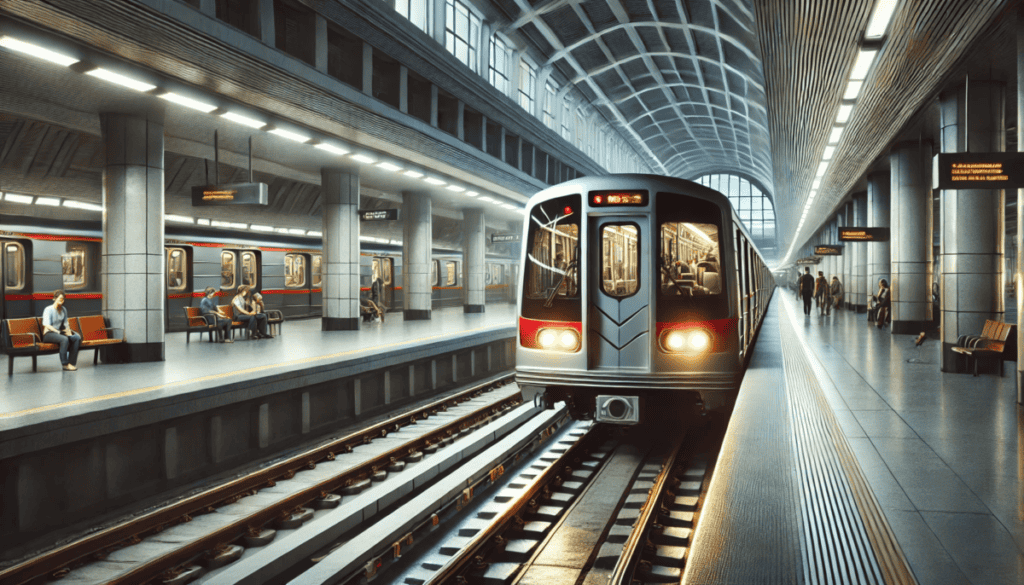

Subway/Metro
Subways, or metros, are underground electric railways designed for high-capacity urban transit. They operate independently of street traffic.
Power Source
Subways are powered by electricity from a third rail or overhead catenary.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet platforms.
- Trips over gaps between the train and platform.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Fatalities from falls onto tracks.
- Severe injuries in collisions or derailments.
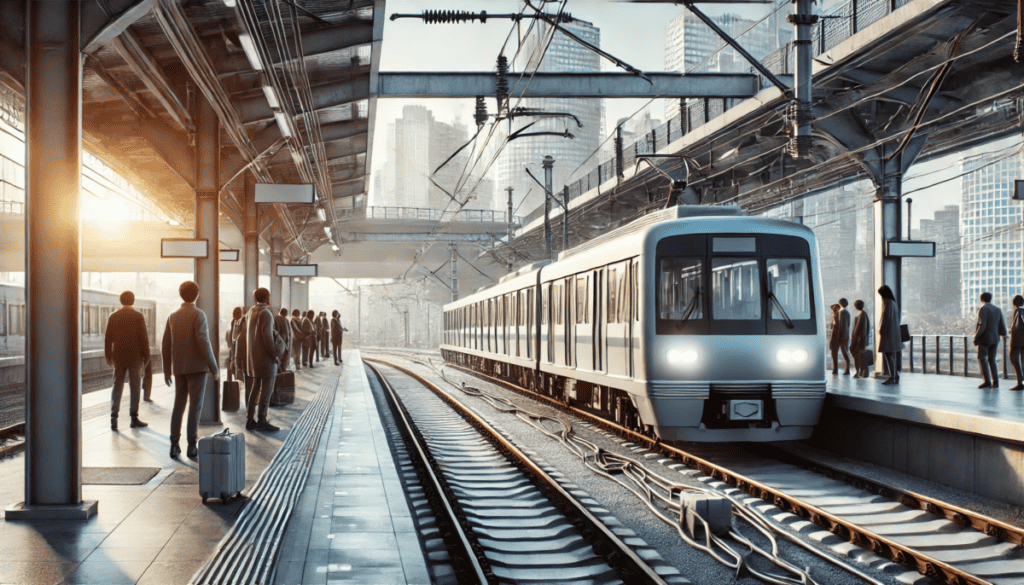

Heavy Rail
Vehicle and System Description
Heavy rail systems are high-capacity urban and regional transit, often operating on exclusive right-of-way tracks.
Power Source
Heavy rail is powered by diesel, electricity from a third rail or overhead catenary.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet platforms.
- Falls down stairs or escalators.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Fatalities from falls onto tracks.
- Severe injuries in collisions or derailments.

Commuter Rail
Vehicle and System Description
Commuter rail services transport passengers between suburban areas and central cities, operating on traditional railway tracks.
Power Source
Commuter rail is powered by diesel, electricity from a third rail or overhead catenary.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet platforms.
- Trips over gaps.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Fatalities from track falls.
- Severe injuries in collisions.

Passenger Transit Ferry
Vehicle and System Description
Ferries transport passengers and sometimes vehicles across bodies of water, providing vital connections in coastal cities and island regions.
Power Source
Diesel engines typically power ferries.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet decks.
- Falls during boarding or alighting.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Drowning incidents.
- Severe injuries from falls overboard.

Monorail
Vehicle and System Description
Monorails run on a single rail, usually elevated, and are known for their sleek design and smooth operation.
Power Source
Electric motors power monorails.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet floors.
- Falls during boarding or alighting.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Falls from elevated platforms.
- Severe injuries in collisions.

Cable Car (Street & Urban)
Vehicle and System Description
Urban cable cars run on steel tracks and are pulled by a continuously moving cable. They are typically used on steep inclines in cities like San Francisco, USA, and Llandudno, UK.
Cable Car systems overlap with Funicular Systems, and often, the term is used for both.
Power Source
Cable cars are powered by an electrically powered central engine house powering the cable.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Falls during boarding or alighting.
- Slips on wet floors.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Falls from moving cars.
- Severe injuries in collisions.

Cable Car (Suspended & Mountainous)
Vehicle and System Description
Mountainous cable cars, often called aerial trams or gondolas, are suspended from overhead cables and used to transport passengers up steep slopes.
Power Source
Powered by electric motors driving the cables.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Falls while boarding or alighting.
- Slips on wet floors inside the cabin.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Falls from heights if safety measures fail.
- Severe injuries in mechanical failures.

Automated People Mover (APM)
Vehicle and System Description
APMs are fully automated, driverless transit systems often found in airports and urban centers.
Power Source
APMs are powered by electricity.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet floors.
- Falls during abrupt stops.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Falls from elevated platforms.
- Severe injuries in system malfunctions.

Bicycle Sharing System
Vehicle and System Description
Bicycle-sharing systems provide bicycles for shared use, allowing users to pick up and drop off bikes at various docking stations.
Power Source
Bicycles are typically human-powered, with some electric-assisted models.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Falls while riding.
- Slips on wet surfaces.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Severe head injuries from falls.
- Fatalities in vehicle collisions.

Motorcycle Taxi
Vehicle and System Description
Motorcycle taxis provide quick, nimble transport for individual passengers, commonly used in densely populated areas.
Power Source
Gasoline engines traditionally power motorcycles, but onboard energy storage and batteries are increasingly used to power them electronically.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Falls while mounting or dismounting.
- Slips on wet roads.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Severe head or body injuries from falls.
- Fatalities in vehicle collisions.

Ridesharing Services
Vehicle and System Description
Ridesharing services connect passengers with private drivers through app-based platforms, offering flexible, on-demand transportation.
Power Source
Ridesharing vehicles are typically powered by gasoline, diesel, propane, or electric engines.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet surfaces while entering or exiting.
- Falls during sudden stops.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Severe injuries from collisions.
- Physical/Sexual assault.
- Fatalities in pedestrian accidents.

Paratransit Vans
Vehicle and System Description
Paratransit services provide transportation for individuals with disabilities or mobility challenges using accessible vans or small buses.
Power Source
Paratransit vehicles are typically powered by gasoline, diesel, propane, or electric engines.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Falls while boarding or alighting.
- Slips on wet floors.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Severe injuries from collisions.
- Fatalities in mechanical failures of accessibility equipment.

Vanpool
Vehicle and System Description
Vanpools involve shared transportation in vans, typically for commuting purposes, reducing the number of vehicles on the road.
Power Source
are typically powered by gasoline, diesel, propane, or electric engines.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet floors.
- Falls during boarding or alighting.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Severe injuries from collisions.
- Fatalities in rollover accidents.

High-Speed Rail
Vehicle and System Description
High-speed rail systems operate significantly higher speeds than traditional rail, often exceeding 150 mph, providing rapid, long-distance travel between major cities.
Power Source
Electric motors power high-speed rail. Electricity is sourced by overhead wires (catenary) or onboard diesel-powered generators.
Common Passenger Injuries
- Slips on wet platforms.
- Trips over gaps between train and platform.
Worst Passenger Injuries
- Severe injuries in derailments.
- Fatalities in collisions at level crossings.
Transit Expert Witness
As public transit systems evolve, the role of transit expert witnesses becomes increasingly vital.
These experts, including light rail consultants and railroad expert witnesses, provide essential insights into the complexities of transit operations, vehicle safety, and accident causation.
They assist in litigation by offering specialized knowledge to determine liability and ensure justice for injured passengers.
A light rail expert witness is indispensable in cases involving light rail vehicles, streetcars, steel-wheeled trolleys, and trams.
Their expertise covers many transit modes and accident scenarios, making them crucial in navigating the intricacies of public transportation litigation.
In conclusion, the need for specialized transit expert witnesses, especially in light rail, underscores the importance of expert witness consulting in achieving fair and accurate legal outcomes.
Their contributions help improve transit safety and accountability, benefiting public transportation systems and passengers.

